**Let me drop a bombshell here—remote IoT access is not just some futuristic tech dream anymore.** It's real, it's happening, and you can do it yourself without breaking the bank. Imagine being able to control your smart home devices from anywhere in the world, all while sipping coffee on your Mac. Sounds too good to be true? Nope. With a Raspberry Pi and a few clever tricks, you can set up remote access to your IoT devices behind a router—completely free! So buckle up, because we're diving into the nitty-gritty of making this happen.
Now, I know what you're thinking—this sounds complicated. Trust me, I felt the same way when I first started tinkering with Raspberry Pi. But here's the deal: once you break it down step by step, it's actually pretty straightforward. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about accessing your IoT devices remotely without paying a dime. By the end of this, you'll be a pro at setting up secure connections between your Mac and your IoT setup.
Before we get into the juicy details, let's clear the air. This isn't just about hacking into your router or doing something shady. It's about leveraging tools that are already available to you. Tools like Raspberry Pi, port forwarding, and dynamic DNS services can turn your Mac into a powerhouse for managing your IoT devices from anywhere. So, are you ready to level up your tech game? Let's go!
Why Remote IoT Access Matters
Let's cut to the chase—remote IoT access isn't just a cool party trick. It's a game-changer for anyone looking to take control of their smart home or IoT projects. Whether you're managing security cameras, automating your lighting, or monitoring environmental sensors, having remote access means you can stay on top of things no matter where you are. Plus, who doesn't love the convenience of controlling everything from their Mac?
Key Benefits of Remote IoT Access
Here's a quick rundown of why remote IoT access is worth your time:
- Convenience: Control your devices from anywhere, anytime.
- Cost-Effective: Set up everything for free using tools like Raspberry Pi.
- Security: Keep your IoT devices safe with encrypted connections.
- Flexibility: Access multiple devices with a single setup.
Understanding the Basics: What You Need
Before we dive into the setup process, let's talk about what you'll need to get started. Don't worry—this isn't rocket science. You probably already have most of the tools you need, and the rest can be picked up affordably.
Hardware Requirements
- Raspberry Pi (any model will work, but Pi 4 is recommended)
- MicroSD card (at least 16GB)
- Power supply for Raspberry Pi
- Your trusty Mac computer
Software Requirements
- Raspberry Pi OS (download it from the official website)
- A dynamic DNS service (we'll cover this later)
- A terminal app on your Mac (it's built-in, so no need to download anything)
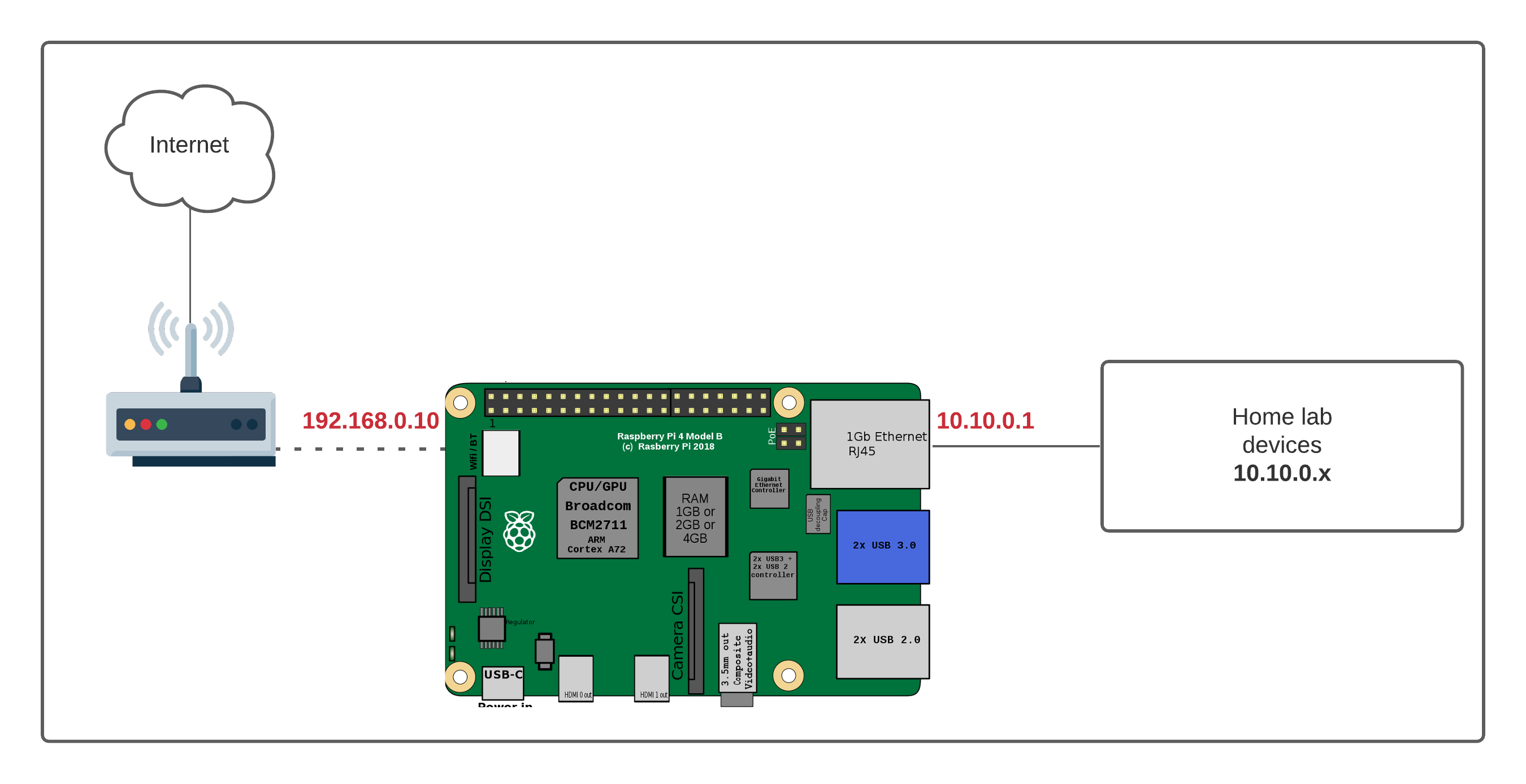
Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi
Alright, let's get our hands dirty. The first step is setting up your Raspberry Pi. This is the brain of your operation, so it's important to get it right. Don't sweat it—it's easier than you think.
Step 1: Install Raspberry Pi OS
Head over to the official Raspberry Pi website and download the latest version of Raspberry Pi OS. Once you've got the file, use a tool like Balena Etcher to flash it onto your microSD card. Pop the card into your Raspberry Pi, power it up, and you're good to go.
Step 2: Configure Your Pi
Now that your Pi is up and running, it's time to configure it. Open the terminal on your Mac and connect to your Pi using SSH. You'll need to know your Pi's IP address, which you can find in your router's admin panel. Once you're connected, update your Pi's software with a simple command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
Connecting Your IoT Devices
With your Raspberry Pi up and running, it's time to connect your IoT devices. This is where the magic happens. Whether you're working with smart lights, cameras, or sensors, the process is pretty similar.
Step 1: Identify Your Devices
Take stock of all the IoT devices you want to connect. Make a note of their IP addresses and any specific ports they use. This info will come in handy later when we set up port forwarding.
Step 2: Configure Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is your secret weapon for accessing devices behind your router. Log into your router's admin panel and set up rules to forward specific ports to your IoT devices. For example, if you're working with a security camera, you might forward port 8080 to the camera's IP address.
Setting Up Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is the key to making your setup accessible from anywhere. Without it, your public IP address could change, leaving you unable to connect. Fortunately, there are plenty of free DDNS services out there to help you out.
Choosing a DDNS Provider
Some popular options include:
- No-IP
- DuckDNS
- FreeDNS
Sign up for one of these services and follow their instructions to set up your domain. Once you've got your domain, configure your Raspberry Pi to update it automatically whenever your IP address changes.
Securing Your Connection
Security should always be a top priority when working with IoT devices. The last thing you want is for someone to hack into your smart home. Luckily, there are plenty of ways to keep your setup safe.
Use SSH for Secure Connections
SSH (Secure Shell) encrypts your data, making it much harder for anyone to intercept. Make sure SSH is enabled on your Raspberry Pi and use strong passwords or SSH keys for added protection.
Enable Firewall Rules
A firewall acts as a gatekeeper, only allowing authorized traffic to pass through. Use a tool like UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) to set up rules that block unwanted connections while letting your IoT devices breathe easy.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even the best-laid plans can hit a snag now and then. If you're having trouble getting your setup to work, don't panic. Here are a few common issues and how to fix them:
Issue 1: Can't Connect to Raspberry Pi
Make sure your Pi is powered on and connected to the same network as your Mac. Double-check the IP address you're using to connect via SSH.
Issue 2: Port Forwarding Not Working
Verify that your router's port forwarding rules are correctly configured. Also, ensure that your ISP isn't blocking the ports you're trying to use.
Advanced Tips for Power Users
If you're feeling adventurous, here are a few advanced tips to take your setup to the next level:
Set Up a VPN
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) adds an extra layer of security by encrypting all your traffic. While not strictly necessary, it's a great option if you're concerned about privacy.
Automate Everything
Use scripts and automation tools to streamline your setup. For example, you could write a script that automatically updates your DDNS domain whenever your IP address changes.
Conclusion
And there you have it—a comprehensive guide to accessing remote IoT devices behind a router with Raspberry Pi for free on Mac. By following these steps, you've unlocked the power to control your smart home from anywhere in the world. Pretty cool, right?
Now it's your turn to take action. Share this article with your friends, leave a comment with your thoughts, and don't forget to check out our other guides for more tech tips. Remember, the world of IoT is yours to explore—so go out there and make something amazing happen!
Table of Contents